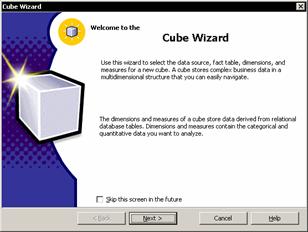
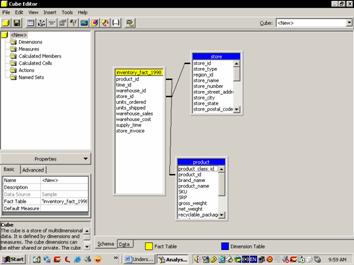
The primary aim of Microsoft was to ease the process of building and using data warehouses. A large number of wizards, editors and tools have been built into the Analysis services to fulfill this objective. The wizards available for use are: The Cube wizard that helps the user build all the structures necessary to create an OLAP cube. It walks the user through the entire cube design and implementation process. The user can map the data sources, create dimensions and define measures using this wizard. The Cube Editor is useful in editing cube structures or in creating new cubes. The simple drag and drop feature makes the operation very easy. It complements the cube wizard and can be used to edit the cubes created in the Cube wizard.
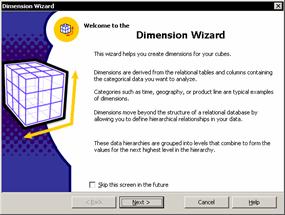
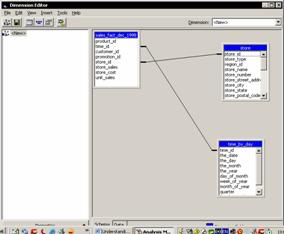
The Dimension Wizard is used to create shared dimensions that can be used by cubes across the data warehouse or a private dimension to be used by a single cube. Data base dimension tables can be mapped to dimension levels and the built in time dimension generator can be used to create a variety of time dimensions based on a date time column in the database. The dimension wizard can also be used to create a star or snowflake schema in the data warehouse. Parent child, virtual or data mining dimensions can be created with ease. The Dimension Editor complements the Dimension wizard and can be used to edit existing dimensions or create new ones. The dimensions can be previewed in the Dimension editor.
The Incremental Update Wizard guides the user through the process of incorporating new data into the cube. This can be done without reloading the aggregations or reloading all data.
The Partition Wizard is used to create partitions in a cube and enable the user distribute and optimize the cube’s data into discrete segments on a single server or on multiple servers. Multiple partition creation is a feature available only in the Enterprise edition of SQL Server 2000. The partition wizard appears when the cube folder is right clicked and partitions >new partitions is selected.
The Storage Design Wizard specifies the storage mode of the cube. Users can design aggregations that are appropriate to the intended use of the cube. The option inbuilt into this wizard enables a tradeoff between response time and storage requirements according to the needs of the application.
{mospagebreak}
The Usage Analysis Wizard helps the user understand how the cube is being used. It displays logged query information such as date, user, query response time and frequency in tabular or graphical format. The Usage Analysis Wizard appears when the cube is right clicked and Usage Analysis wizard is selected.
The usage based optimization wizard is used to tune cube performance based on user’s actual usage of the cube. The Wizard can be directed to create aggregations for improving performance based on any combination of users, the number of times a query is executed, query response time, the mode of data storage or the data range. The Usage based optimization wizard opens when the cube in the left pane of the Analysis manager is clicked and Usage-based optimization wizard option is selected.
The Calculated cells Wizard allows the user define a subsection of the cube (called sub-cube) and to create calculated cells whose value is determined by a Multidimensional Expressions (MDX) formula. The function of the calculated cell is similar to that of a custom member except that calculated cells can affect specific cells within a cube. This allows for finer control for financial and statistical calculations. The Calculated cells wizard can be accessed by right clicking the Calculated Cells folder in the right pane of the Cube editor.
The Action Wizard is used to create actions associated with the cube or the portion of a cube.

Actions can be triggered on a cube or portions of a cube automatically and the user can pass the selected item as a parameter to an operation. For instance if the user selects an action on a dimension member, it automatically opens the Internet browser so that the member page can be accessed. Right Click on the Actions folder in Cube Editor’s right pane to invoke the action wizard.
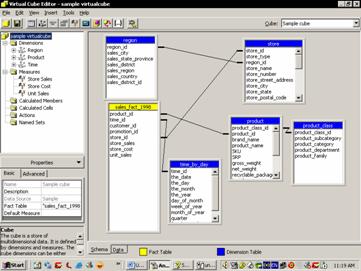
The Virtual Cube wizard enables user join cubes, select dimensions and measures form which to create a virtual cube. Single queries can be routed to multiple cubes on the same or different servers using the Virtual cube wizard. The virtual cube is similar to the regular cube in appearance but it does not require the storage space that a regular cube needs. It is similar to views that join tables together in the relational database. The Virtual cube wizard can be accessed by right clicking on Cube in the Analysis Manager right pane and selecting New Virtual Cube…
The Virtual Cube Editor enables users to edit virtual cubes with drag and drop functionalities. It complements the Virtual Cube wizard and can be accessed by right clicking on a cube in the right pane of the Analysis manager and selecting edit.
{mospagebreak}
The Mining model Wizard is used to create data mining models from OLAP and relational data sources. Different data mining techniques can be specified to build the model. Models based on OLAP provide the option of defining a dimension and a virtual cube for analyzing mining model results. Mining model wizard can be accessed by right clicking on the Mining models folder under the Database folder and selecting Mining models.
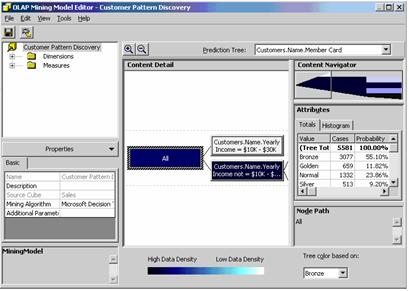
Mining model Editors are of two kinds. OLAP data mining models and relational data mining models. Existing mining models can be edited using drag and drop techniques and browsing the results of the mining models.
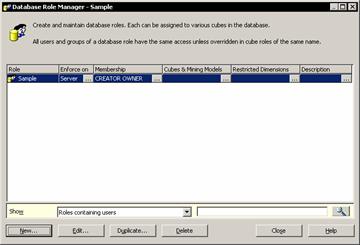
Data views are views for cubes, dimensions and data mining models within the Analysis manager. This helps the user check on the designs without switching between applications. OLE DB data source locator Integration is a Microsoft Data Source Locator component for selecting OLE DB or ODBC data sources. Role managers are of two kinds. Database Role Manager and Cube Role Manager are two role managers in the Analysis Services that help the user create roles and control users’ access to cubes and their component parts.
Functions from Excel and Visual basic applications are automatically registered if they are installed on the computer on which Analysis Services is installed. The Applications expressions library of the Analysis services enables the user include many functions from Microsoft Visual basic. These are automatically registered when defined. Server side cache is the Analysis Server cache and it stores user queries, meta data and data. Cached queries and meta data can be used to answer new queries by calculating answers from the cached data. Client applications connect to the Analysis server through the PivotTable Service component. The client application receives meta data with data from the server in response to queries and calculates the answer by using the data in client side cache without sending new queries to the server.
[catlist id=181].