SQL Server Management Studio
SQL Server Architecture and Components
What strikes the developer is the absence of the SQL Enterprise Manager in the interface. The SQL Server Management Studio offers functionality enhancements and a new look and feel to the application. It has been implemented using Winforms and .NET framework and is completely different from the Microsoft management console and looks more like the Visual studio Interactive development Environment(IDE).
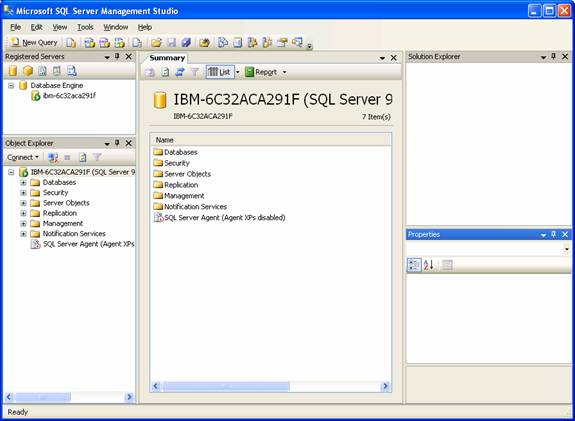
The design allows administration and programming features through the same interface focusing upon consistency of experience. A significant improvement is the introduction of non modal dialog boxes. These boxes allow the comparison of content and are resizable and permit switching between dialog boxes for performing multiple actions in parallel.
The tool is backward compatible and manages instances of SQL 2000. It can also be used to control Server Mobile Edition. A number of SQL based server utilities can also be launched from the Tools menu such as the SQL Profiler and the Database Tuning Advisor.
The SQL Server Management Studio is modular and contains a number of windows that can be docked or remain floating
1. The Object Explorer enables registration, browsing and management of servers and their components. Objects are arranged in hierarchies and can be ordered according to the type or filtered based on their name, schema or date. The information about the objects are available in the Summary view window or in the Reporting Services. The new asynchronous refresh for the windows allows access to manipulate loaded objects without waiting of the processes to be completed by others. The script option allows administrative tasks to be scripted with ease.
This option is available in the menu of the properties window. Once scripted the task can be scheduled for later execution and this automatically creates an SQL Server Agent job. Functions and stored procedures can be created with assisted editors. Maintenance plans node serves as a replacement for the Database Maintenance Wizard and integrates with the Data Transformation services. This enables design of workflow for a variety of maintenance tasks.
2. Servers can be registered and connections can be recorded per server with all associated settings. Server registration can also be exported form one instance of the SQL to another.
3. The Solution Explorer implements the programming paradigm of the Visual Studio in SQL Server. It groups pieces of related code and integrates with Visual SourceSafe for supporting version control. However, the Solution Explorer does not offer the ability to compile programs written in .NET languages. It supports T-SQL and XML Query Language scripts, XML for Analysis services and MDX cube calculations or DMX operations.
4. The Query Editor is a combination of the Query Analyzer and Analysis Manager. It has the ability of executing queries written in T-SQL, XMLA, MDX and DMA against SQL server mobile edition and Analysis Services in connected and disconnected scenarios. It integrates the Visual SourceSafe version control. Query execution plan can be displayed with estimated and actual plans and the showplan can be saved as an XML document, making it portable ad simplifying logistics for troubleshooting. The Query Editor can also be run in the SQLCMD mode. It can be accessed both from the file menu and the Query menu.
5. The Template Explorer helps in creating queries based on existing templates.
6. Dynamic Help is available from the help menu and from the context sensitive help feature.
[catlist id=178].
