.Oracle Apps 11i Tutorials : Asset Management – Asset Book Positioning
Oracle Assets is a complete asset management solution that maintains property and equipment accurately to help you the best accounting and tax strategies.
- You can add, transfer, and retire assets.
- You can adjust for a single asset, group of assets, or financial information.
- Oracle assets adapts to various countries’ tax and accounting laws to accommodate fluctuating economies, unplanned depreciation, and other unforeseen circumstances.
- Oracle assets provides reports that you can use to inform the fixed asset manager of additions, transfers, retirements, or other unrecorded changes, ensuring that the asset inventory remains accurate.
- At any time, you can print these reports or you can view descriptive or financial information about assets online.
Overview
Assets Integration
Oracle Assets integrates with Oracle Payables, Projects, and General Ledger to provide asset management information.
1. It uses supplier information from Oracle purchasing, UOM and items from Oracle Inventory, and employees from Oracle HR.
2. Also interfaces directly with the Application Desktop Integrator.
3. You can use Mass additions to load into Oracle Assets invoice and asset information from any feeder system, such as Oracle Payables or another payables system.
4. You can import CIP assets from Oracle projects.
5. Oracle Assets eases GL integration by automatically producing asset journal entries for the GL system.
Asset Life Cycle
You add assets to the Oracle Assets system through manual additions or transactions that flow through the FA_MASS_ADDITIONS table.
Asset Books
Positioning
Define asset books to store financial information for a group of assets. Use 3 types of asset books:
1. Corporate A book to track financial info for your balance sheet.
2. Tax A book to track financial info for tax reporting authorities.
3. Budget A book to track planned capital expenditures.
Define corporate books first, and then tax and budget books.
To define an Asset Book:
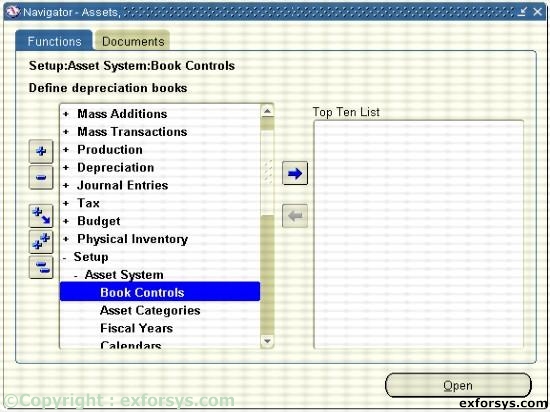
Figure1. Navigate to define an Asset Book.
1. Enter a book name and description for your book.
2. Choose a Corporate, Tax, or Budget book class. If defining a Tax or Budget book, you must associate those books with a Corporate book. If the book you are defining is a corporate book, it will automatically be associated with itself.
3. Enter calendar info.
4. Enter accounting rules.
5. Enter natural accounts.
6. Enter journal categories.
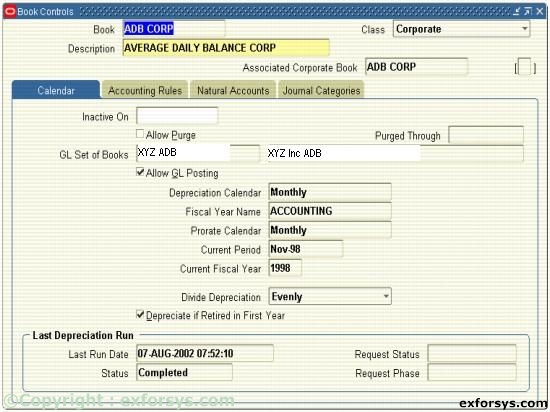
Figure 2(a). Define a Corporate Asset Book.
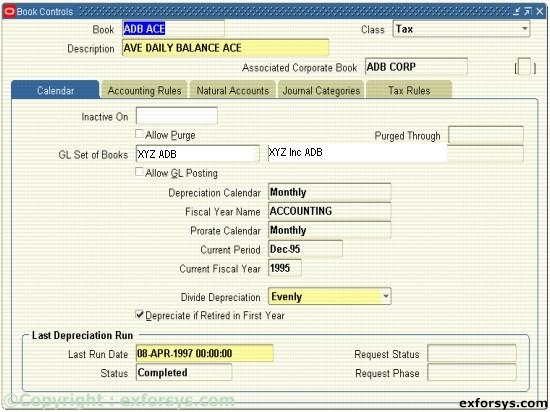
Figure 2(b). Define a Tax Asset Book.
{mospagebreak}
.
.
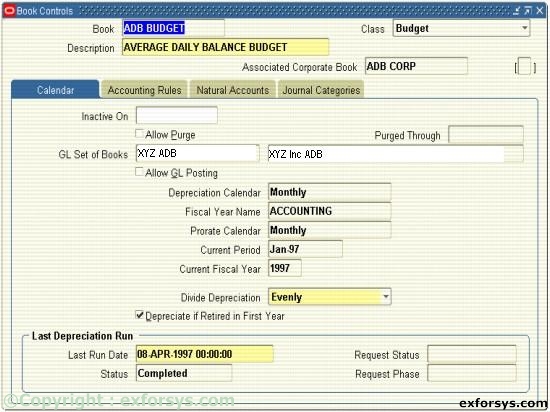
Figure 2(c). Define a Corporate Asset Book.
You must complete each region for every book you define regardless of whether the information will be used or not.
Asset Categories Positioning
All assets are required to have an asset category. Asset categories group assets that share financials accounts and usually depreciate using the same rules. Oracle Assets uses this information to provide default values at the time an asset is entered into the system.
Figure 3. Navigate to Asset Categories.
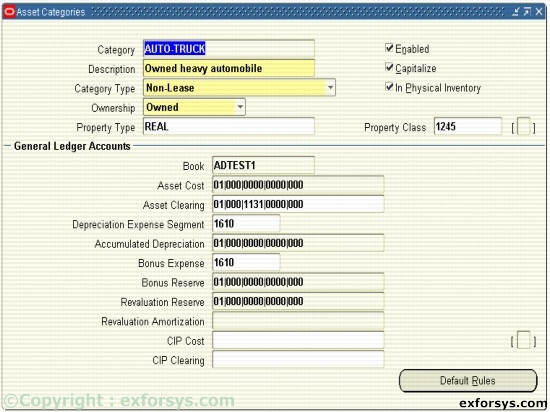
Figure 4. Asset Categories.
[catlist id=183].
