The virtual cube editor is used to maintain the calculated members in virtual cubes. The Virtual cube Editor provides a single click access to Calculated Member Builder and the Import Calculated Members dialog box, which can be used to import calculated members into the virtual cube.
Creating a Calculated Member in a Virtual Cube
In the Analysis Manager tree pane, right-click the virtual cube, and then click Edit.
In Virtual Cube Editor, on the Insert menu, click Calculated Member.
|
|
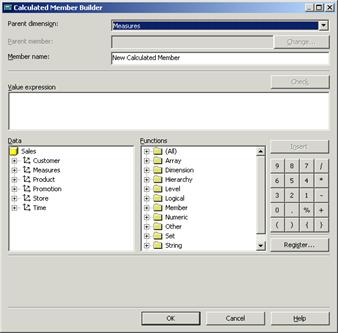
In Calculated Member Builder, in the Parent dimension box, select the dimension that will include the calculated member. Select Store.
In the Parent member box, specify the member that will include the calculated member.
In the Member name box, type a name for the calculated member as Store Profit.
In the Value expression box, construct an expression to produce the values of the calculated member.
[Measures].[Store sales]-[Measures].[Store Cost]
Use any combination of the following methods to add to the expression:
Drag items from the Data and Functions boxes.
Click an item in the Data or Functions box, and then click Insert.
Click the arithmetic operator and number buttons.
Type.
(Optional.) To register additional function libraries, click Register.
To close Calculated Member Builder, click OK.
To save the calculated member, in Virtual Cube Editor, on the File menu, click Save.
Importing a Calculated Member into a Virtual Cube
While importing a calculated member into a virtual cube, it is important that the syntax of the Calculated member is validated. Syntax errors can occur due to incorrectness of the expression or that the value expression includes a measure, dimension or other objects which are not available in the virtual cube. The calculated member will not be displayed to end users so long as the error is not rectified. The syntax errors can be corrected by invoking the Virtual cube Wizard from within the Virtual cube Editor, or by clicking Structure(Wizard) on the Edit menu of the Virtual Cube Editor. The calculated member can also be edited in the Calculated Member builder and re-imported.
{mospagebreak}
If the user imports a calculated member that bears the same name as an existing calculated member in the cube, the imported member is renamed automatically. The new name will be the old name plus a numeric suffix.
Calculated members can be imported only from cubes that are in the same database as the virtual cube.
In the Analysis Manager tree pane, right-click the virtual cube, and then click Edit.
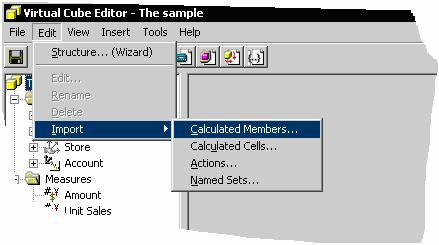
In Virtual Cube Editor, on the Edit menu, point to Import, and then click Calculated Members.
|
|
In the Import Calculated Members dialog box, the calculated members are displayed. The user can select the check box beside the calculated member, and then click OK. (To select all the calculated members in a cube, select the check box beside the cube.)
In Virtual Cube Editor, on the File menu, click Save.
To edit a calculated member in a virtual cube
In the Analysis Manager tree pane, right-click the virtual cube, and then click Edit.
In the Virtual Cube Editor tree pane, right-click the calculated member, and then click Edit. The Calculated member builder dialog box appears.
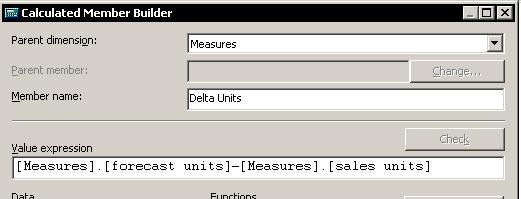
In Calculated Member Builder, in the Parent dimension box, select the dimension that will include the calculated member, or select Measures.
|
|
In the Parent member box, specify the member that will include the calculated member. Click Change to select a member other than the displayed member.
In the Value expression box, construct an expression to produce the values of the calculated member. Use any combination of the following methods to add to the expression:
Drag items from the Data and Functions boxes.
Click an item in the Data or Functions box, and then click Insert.
Click the arithmetic operator and number buttons.
Type.
To close Calculated Member Builder, click OK.
To save the calculated member, in Virtual Cube Editor, on the File menu, click Save.
In this lesson we learnt about Virtual cubes, the benefits of creating and using such cubes and also how to create calculated members for such cubes. Virtual cubes can effectively remove dimensions or measures from a cube, combine measures from multiple cubes that share at least one dimension or both.
[catlist id=181].